Lyme disease is an increasingly common tick-borne illness that can lead to serious, long-term health problems if not treated early. In this article, we explore what causes Lyme disease, the stages and symptoms, conventional treatment options, biomagnetism as a complementary therapy, and how to prevent and manage recurrence. Whether you want to better understand the disease or explore holistic modalities like biomagnetism therapy for Lyme disease, this guide has you covered.

What Causes Lyme Disease?
Lyme disease is caused by bacteria of the Borrelia genus—most commonly Borrelia burgdorferi—transmitted to humans through the bite of infected ticks. Understanding the cause is crucial to preventing infection and recognizing symptoms early.
The Tick Vector and How Infection Occurs
- Types of ticks: The disease is primarily carried by deer ticks (black-legged ticks) in the U.S., while Europe has related species like Borrelia garinii and Borrelia afzelii (Mayo Clinic).
- Lifecycle stages: Ticks go through larval, nymph, and adult phases. Nymphs are small and hard to detect, yet account for many transmission cases.
- Time of attachment matters: A tick generally needs 36–48 hours attached to transmit the bacteria.
Environmental & Risk Factors
- Habitats: Wooded, grassy, and brushy areas increase exposure risk.
- Seasonality: Most common in spring through autumn (FDA).
- Pets & livestock: Animals can carry ticks closer to human environments.
Stages & Symptoms of Lyme Disease
Lyme disease may present itself differently, and symptoms can appear days or weeks after a tick bite.
Early Stage (Localized Infection)
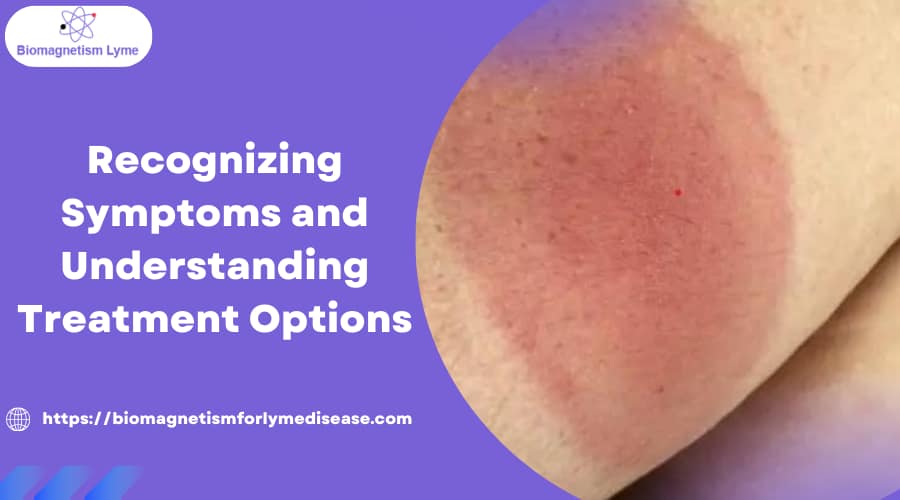
- Erythema migrans rash: A red, expanding “bull’s-eye” rash appears within 3–30 days.
- Flu-like symptoms: Fever, chills, fatigue, muscle aches, headache.
Early Disseminated Stage
- Spread of bacteria: Weeks to months after infection, bacteria spread to joints, heart, and nervous system (Cleveland Clinic).
- Common signs: Multiple rashes, Bell’s palsy, irregular heartbeat, tingling sensations.
Late Stage (Chronic Lyme)
Some individuals might have symptoms even for months to years after the infection. It includes:
- Joint complications: Lyme arthritis, especially in knees (Hopkins Lyme Disease Center).
- Neurological issues: Brain fog, memory problems, and chronic pain.
Conventional Treatment Options
Antibiotic Treatments
- First-line oral antibiotics: Doxycycline, amoxicillin, cefuroxime (10–14 days, sometimes longer).
- IV antibiotics: For severe neurological or cardiac Lyme cases.
Post-Treatment Lyme Disease Syndrome (PTLDS)
- Even after treatment, 5–15% experience lingering symptoms.
- Management focuses on rest, symptom relief, and supportive care.
Biomagnetism as a Complementary Treatment Option
What Is Biomagnetism Therapy for Lyme?
Biomagnetic therapy involves placing pairs of magnets with opposite polarity on the body to balance pH levels and promote healing. It may reduce inflammation, support detox, and strengthen immunity.
How It Complements Conventional Treatment
- Works alongside antibiotics, not as a replacement.
- Helps reduce chronic pain, fatigue, and brain fog.
- Recommended in multiple sessions for lasting results.
Safety & Considerations
- Safe, drug-free, and non-invasive.
- Best practiced by certified biomagnetism therapists.
- Evidence is largely anecdotal but promising for symptom relief.
Preventing Lyme Disease & Recurrence
Tick Bite Prevention
- Wear long clothing and light colors.
- Use repellents like DEET or permethrin (FDA).
- Stay on trails and avoid dense brushes.
Early Detection
- Check for ticks daily after outdoor activity.
- Remove ticks promptly with fine tweezers.
- Watch for rashes and flu-like signs.
Post-Treatment Wellness
- Eat an anti-inflammatory diet.
- Support healing with therapies like biomagnetism treatment for Lyme.
- Stay consistent with medical follow-ups.
